Sunscreen Isn’t Just for the Beach: Why You Need It Every Day
The Importance of Daily Sunscreen
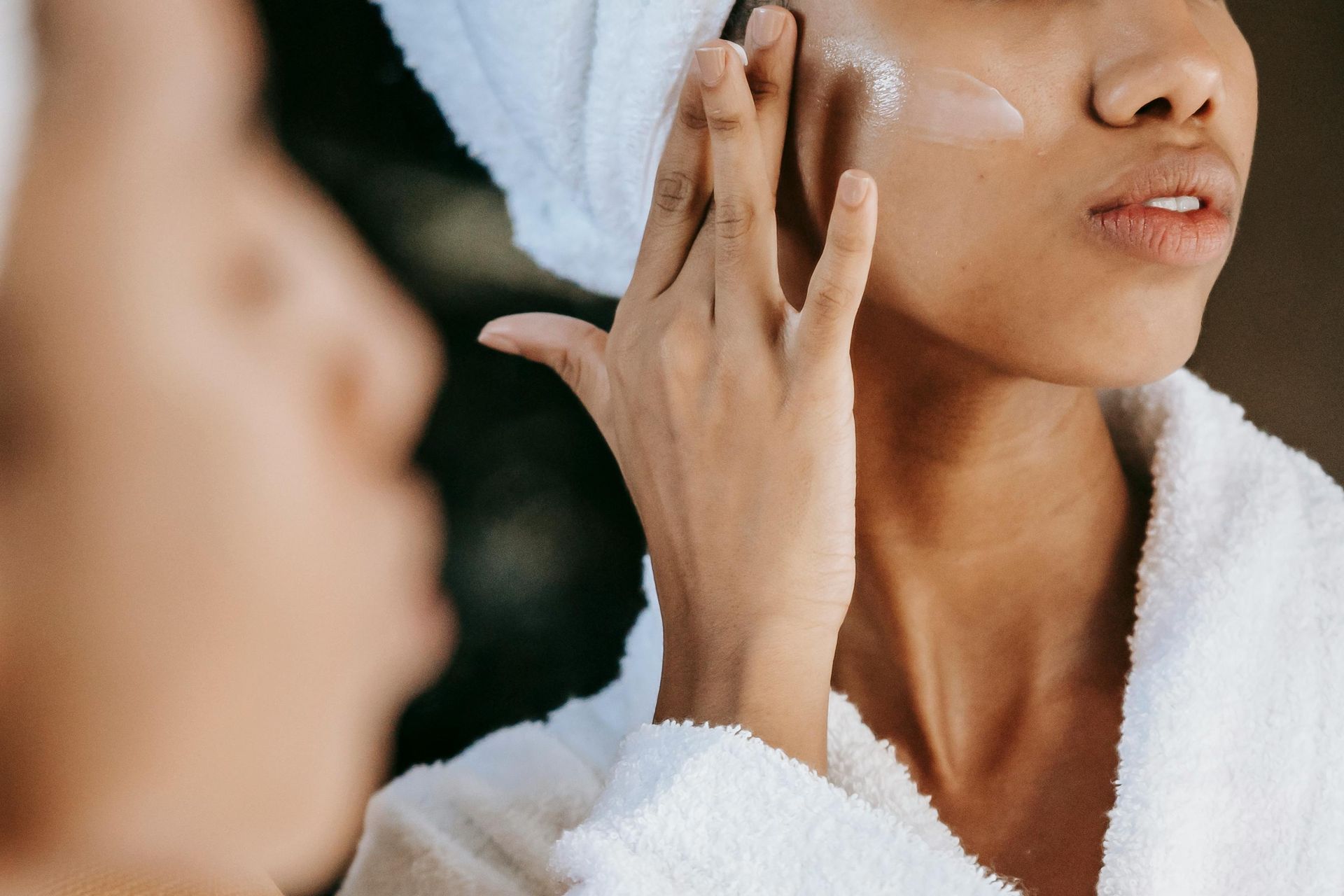
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is the leading cause of skin cancer and premature aging. Daily use of sunscreen is one of the most effective ways to protect your skin from its harmful effects.
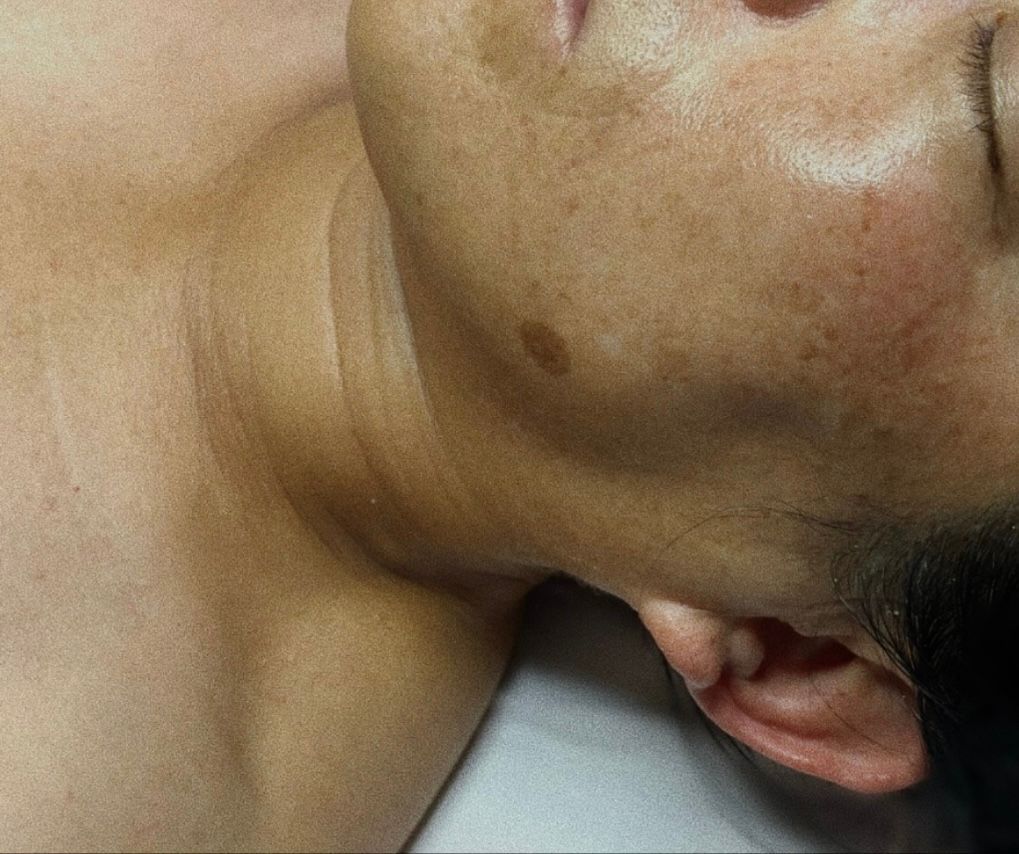
According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, UV radiation is a proven carcinogen—exposure to these rays alters DNA and significantly increases the risk of skin cancer. In addition to its cancer-causing effects, UV radiation is responsible for approximately 80–85% of visible skin aging. It weakens collagen and elastin fibers, which are already compromised as we age, leading to wrinkles, sagging, and an uneven skin texture.
Forms of UV
There are two main forms of UV radiation that affect our skin: UVA and UVB.
UVA Radiation
UVA radiation also know as aging rays, penetrate deep into the skin and accelerates aging by causing genetic damage and cell death. This damage wears down our collagen and elastin fibers which contributes to wrinkles and sagging skin. It is important to note that UVA can penetrate glass and clouds, making it crucial to wear sunscreen even on cloudy days or when you're indoors!
UVB Radiation
UVB radiation, also known as burning rays, are responsible for sunburn, as well as tanning, aging and cancer.
Both types of UV radiation can damage the skin on different levels, which makes it essential to use a broad-spectrum sunscreen that filters both UVA and UVB rays.
Cumulative Sun Damage
A common misconception is that sunscreen only needs to be applied during prolonged outdoor activities, such as going to the beach or spending the day at the park. However, sun damage is cumulative—meaning that even short periods of daily exposure add up over time. UV radiation triggers the formation of free radicals, which alter DNA and increase the risk of cancer. This same process also breaks down collagen and elastin, causing fine lines, loss of firmness, and hyperpigmentation. Although the effects of sun damage may not be immediately visible, they are long-lasting and difficult to reverse, making prevention a critical part of any anti-aging routine.
Physical vs Chemical Sunscreen
- Physical (mineral) sunscreens work by creating a barrier that reflects UV rays away from the skin. Look for active ingredients like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide.
- Chemical sunscreens absorb and neutralize UV rays. Common ingredients include avobenzone, octisalate, octocrylene, and others.
Additional Sun Protection
In addition to applying sunscreen daily, incorporating the following sun-protective habits will further safeguard your skin:
- Seek shade whenever possible, especially during peak sunlight hours
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants, skirts, or dresses to cover exposed skin.
- Use a wide-brimmed
- Choose sunglasses that block both UVA and UVB rays
- Avoid outdoor activities during times of high UV index—aim for early mornings or late afternoons.
Conclusion
Protecting your skin from the sun isn’t just about avoiding a sunburn—it’s a long-term investment in your health and appearance. Daily sunscreen use, along with other protective measures, is one of the most effective ways to prevent skin cancer, premature aging, and irreversible sun damage. By making sunscreen a non-negotiable part of your morning routine, you're not just preserving your skin’s youthful glow—you're actively protecting your future self.