Exfoliation 101: The Ultimate Guide for Glowing, Healthy Skin
Exfoliation: What It Is, How Often to Do It, and How to Choose the Best Option
When it comes to skincare, exfoliation is one of those buzzwords that’s often mentioned—but not always fully understood. Done right, exfoliation can transform your skin, giving it that smooth, glowing finish. But if done incorrectly, it can lead to irritation, breakouts, or even long-term damage.
So, what exactly is exfoliation, how often should you be doing it, and which type is best for your skin? Let’s break it down.
What Is Exfoliation?
Exfoliation is the process of removing dead skin cells from the surface of your skin. Our skin naturally sheds these cells every 28–40 days, but factors like aging, environment, and product buildup can slow the process. When dead cells pile up, skin can look dull, rough, or congested.
There are two main types of exfoliation:
- Physical Exfoliation: Uses scrubbing particles, brushes, or tools to manually remove dead skin (e.g., scrubs with microbeads, exfoliating mitts, cleansing brushes).
- Chemical Exfoliation: Uses acids or enzymes to dissolve dead skin cells (e.g., AHAs like glycolic acid, BHAs like salicylic acid, or fruit enzymes).
How Often Should You Exfoliate?
This depends on your skin type, method used, and product strength, but here’s a general guide:
- Oily/Acne-Prone Skin: 2–3 times per week. BHAs (like salicylic acid) are ideal because they penetrate into pores and reduce oil buildup.
- Dry or Sensitive Skin: 1–2 times per week. Choose gentle chemical exfoliants (like lactic acid or fruit enzymes) or ultra-fine physical scrubs.
- Normal/Combination Skin: 2–3 times per week, alternating between physical and chemical if needed.
Note: Over-exfoliation can lead to redness, sensitivity, and breakouts. Always listen to your skin—if it feels irritated, take a break.
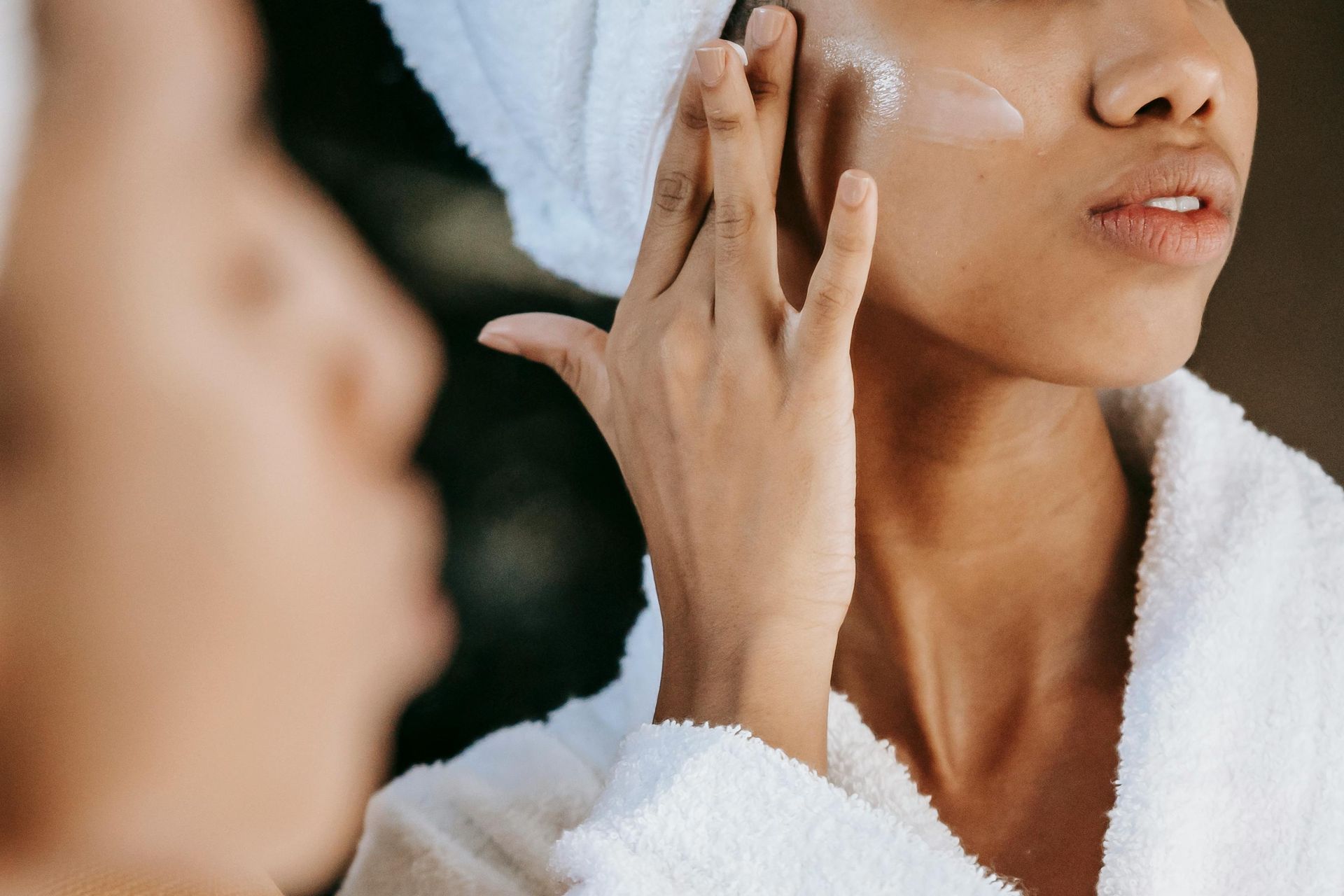
How to Choose the Right Exfoliation Method
Here’s how to match the method to your skin type and concerns:
1. Physical Exfoliants
Best for: People who like a “clean,” scrubbed feeling and have non-sensitive, resilient skin.
Examples:
- Sugar scrubs
- Microdermabrasion
- Konjac sponges
Tips:
- Use light pressure.
- Avoid large, jagged particles (like walnut shell) that can cause micro-tears.
- Use no more than twice a week.
2. Chemical Exfoliants
Best for: Sensitive, acne-prone, mature, or uneven skin tones.
- AHAs (Alpha Hydroxy Acids) – Great for dry or aging skin. They exfoliate the surface and improve hydration and tone.
-
Glycolic acid
(strongest)
- Lactic acid (gentler)
- BHAs (Beta Hydroxy Acids) – Best for oily or acne-prone skin. They go deeper into pores to unclog and reduce inflammation.
- Salicylic acid
Tips:
- Start slowly (1–2 times/week) and work up.
- Use SPF daily—acids can increase sun sensitivity.
- Don’t mix too many actives (like retinoids or vitamin C) unless advised.
3. Enzyme Exfoliants
Best for: Super sensitive skin types.
These are derived from fruits like papaya (papain) or pineapple (bromelain) and gently dissolve dead skin.
Tips:
- Great for rosacea-prone or easily irritated skin.
- Can be used once or twice a week without much risk of irritation.
Final Thoughts
Exfoliation is a powerful tool in your skincare routine, but like anything, it requires balance. The key is consistency and customization—choose the method that fits your skin type, start slowly, and always follow up with hydration and sun protection.
Remember: Glowing skin is not about scrubbing harder—it's about exfoliating smarter.